Total knee replacement after a torn meniscus: what you should know
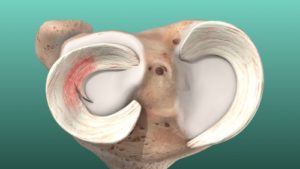
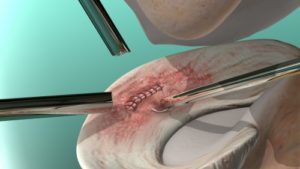
By Grace Lieberman A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. The meniscus cartilage in your knee acts as a shock absorber between your shin and thigh bones. It can tear when someone twists their knee while bearing weight, usually through physical activity. Athletes and older people who have experienced years of [...]
read more